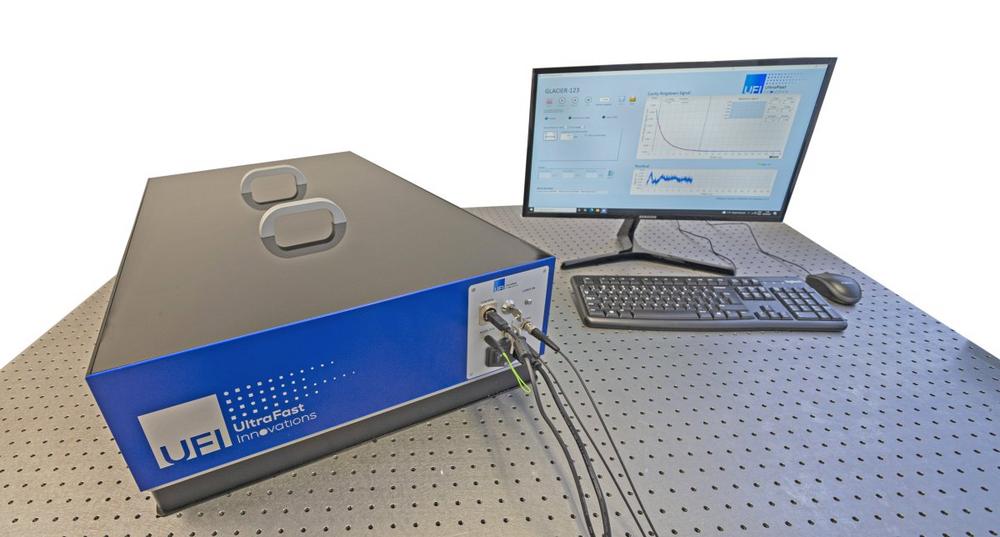
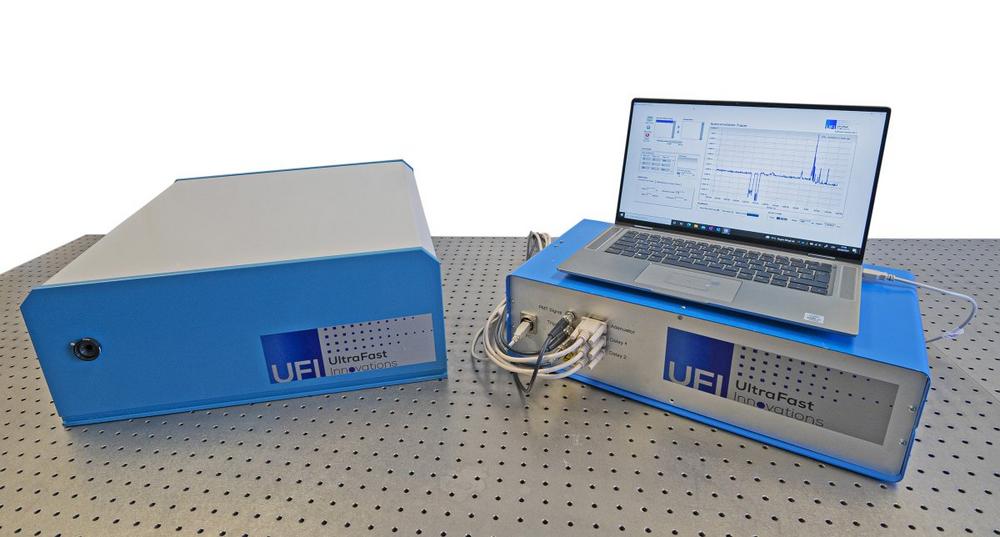
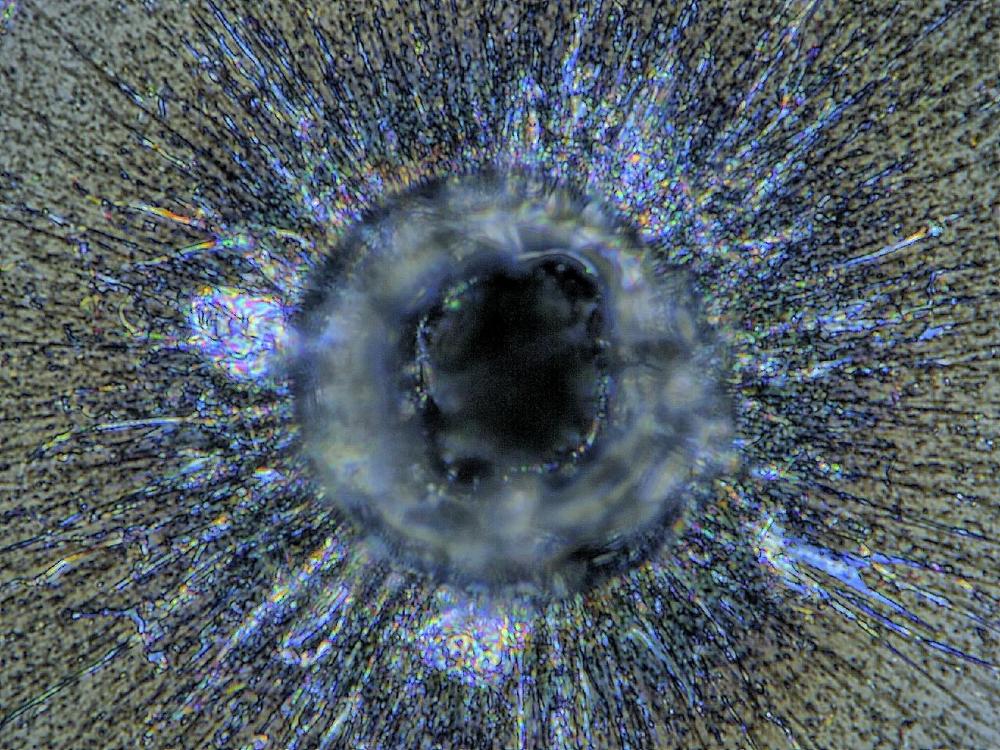
Laser Induced Damage Threshold (LIDT) of optical components, including but not limited to highly dispersive mirrors, is an acute issue in high-energy/high-power ultrafast laser systems largely influencing not only their life expectancy, but also ultimate performance and possibilities for further output power/energy scaling. Since this question became one of the most frequently asked ones in […]
Read More